EAN rule is also called as 18 electron rule. In 1920s English scientist Nevil V.Sidgwick made the assumption in various metal complexes, the metal use to surround with the ligands as much as it can that the resulting electron count is equivalent to noble gas configuration found in the same period in which metal is located. This rule appears to hold for various transition metal complexes such as metal carbonyls and various organometallic compounds.
Why 18 electron rule?
EAN Rule is also known as 18 electron rule if the total electron count of the central metal and the attached ligands is equal to 18. For example, cobalt complex [Co (NH3)6]3+. (6 for Co3+ and 2 × 6 = 12 for 6 NH3)= 18 electrons. So this complex follows EAN Rule. Noble gases were regarded by the scientists as a symbol of stability that’s why now referred as 18-electron rule or effective atomic number rule.
Effective Atomic Number in Different Compounds
So in context of above definition we can explain EAN concept for coordination compounds. This concept explain the stability and possibility of coordination compounds formation. Based on this concept the complex compound can only be formed when it acquire the noble gas electronic configuration. Here is an overview of different d block elements.
| D-Block Element | Atomic No. | Nearest Noble gas | Nearest Noble gas Atomic No. |
| 1. Scandium | 21 | Kr | 36 |
| 2. Vanadium | 23 | Kr | 36 |
| 3. Chromium | 24 | Kr | 36 |
| 4. Manganese | 25 | Kr | 36 |
| 5. Zirconium | 40 | Xe | 54 |
| 6. Yttrium | 39 | Xe | 54 |
| 7. Niobium | 41 | Xe | 54 |
The Formula of EAN Rule:
EAN = Atomic number (Z) – Oxidation number + n× y
EAN= Z – x + n*y
Z= Atomic no. of metal
x = Oxidation state of metal in complex
n= Total no. of ligands
L = no of electrons donated by 1 ligand
This rule tells about
- Stability of coordination compounds.
- The metal in the complex will continue to accept the electrons from the ligand till the total electron count in the metal ion is equal to the atomic no. of the noble gas of the same series
18-electron rule Vs effective atomic number rule
Although these two words are used interchangeably but there are specific differences between them. The 18-electron rule says that compound must have 18-electron in its valence shell to be stable. But the effective atomic rule suggest that metal should have total electron count of the noble gas of the same period as discussed above.
EAN Rule Examples
Calculate the effective atomic number for Ni in Ni (CO)4 complex?
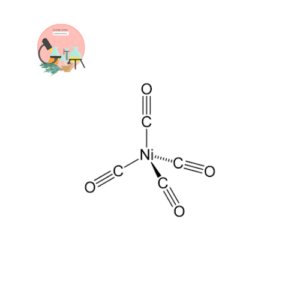
- The atomic no. of Nickel is
- Carbonyl (CO) is a monodentate ligand (donate two electron per ligand)
- Oxidation state of Nickel is 0
- The number of electrons donated by one ligand is 2
- Total no. of ligands is 4
EAN for the Nickel = Atomic number of Nickel (Z) – oxidation state of Nickel (x) + the number of electrons donated by one ligand (n)* Total no. of ligands (y).
EAN of Nickel (Ni) = 28 -0 +2*4
EAN of Nickel (Ni) = 36
Calculate the effective atomic number for Co in Co(dien)2 complex?
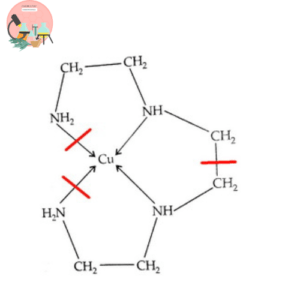
- The atomic no. of Nickel is
- Diethylenetriammine (dien) is a tridentate ligand (donate 6 electron pr ligand)
- Oxidation state of Cobalt is 3
- The number of electrons donated by one ligand is 2
- Total no. of ligands is 2
EAN for the Cobalt = Atomic number of Nickel (Z) – oxidation state of Nickel (x) + the number of electrons donated by one ligand (n)* Total no. of ligands (y).
EAN of Cobalt (Co) = 27 -3 +6*2
EAN of Cobalt (Co) = 36
36 is the noble gas electronic configuration of Kr
Calculate the effective atomic number for Mn in Mncl(CO)5 complex?
- The atomic no. of Maganese is
- Carbonyl (CO) is a monodentate ligand (donate two electron per ligand)
- cl donate two electron (Monodentate)
- Oxidation state of Maganese is 1
- The number of electrons donated by one ligand is 2
- Total no. of ligands is 5+1=6
EAN for the Maganese will be = Atomic number of Maganese (Z) – oxidation state of Maganese (x) + the number of electrons donated by one ligand (n)* Total no. of ligands (y).
EAN of Maganese (Mn) = 25 -1 +2*6
EAN of Maganese (Mn) = 36
Application of EAN Rule
- By using this rule magnetic property of different complexes can be predicted, molecules which obey this rule are diamagnetic. e.g Co(NH3)6 is diamagnetic. Those which donot follow this rule is paramagnetic in character.
Limitations of EAN Rule
- Many complexes are quite stable even though they does not obey E.A.N. rule.
- Stability of complex.
- It does not gives geometry of complexes.
- Not all complexes follow this rule.